Issue #11 - What to Expect in 2024 for AI & LLMs
Anticipated Developments and Wildcard Predictions for Enterprises
As we approach the end of the year, it's time for the traditional ritual of forecasting what the next year holds.
AI in 2023 felt like being strapped into a F1 car, with the foot on the accelerator all the way through!
As we look ahead to 2024, some predictions can be reasonably made, while others remain more challenging to foresee.
I have decided to split my predictions into - ‘Anticipated Developments’ and ‘Wildcard Predictions’.
So here goes.
Anticipated Developments
1. Open Source Foundational Models in Enterprises
In 2024, I foresee a trend where enterprises increasingly lean towards open source foundational models for their AI/LLM needs. This year, open source models have remarkably caught up with their proprietary counterparts in terms of capabilities. What's most striking is the speed of this evolution; within just a year, these models have made significant strides.
Mixtral 8x7B, the latest model from Mistral AI, is a significant advancement in open-source LLMs. It supports 32k tokens, offers improved code generation, and matches or outperforms GPT-3.5 on most standard benchmarks. Despite having 46.7 billion parameters, Mixtral 8x7B operates like an ensemble of eight models, making it efficient and adaptable. It is significantly cheaper than both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, making it a cost-effective option for enterprise.
However, transitioning to Mixtral 8x7B, especially for those who previously used models like ada v2 for embedding, may require some adjustment. Despite this, Mixtral 8x7B represents a promising development in the AI field, offering powerful and efficient tools for a variety of applications.
The appeal for businesses in adopting open source models lies in their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Companies can now access AI tools that offer high-level functionalities similar to established models like Claude 2.0, GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 but without the high cost. This shift is crucial for businesses looking to integrate AI solutions tailored to their specific needs, ranging from customer interaction enhancements to advanced data analytics.
“I anticipate that the enterprise sector will increasingly recognise the value of open source AI models in 2024. The one major advantage that gets overlooked in open-source LLMs is the removal of unnecessary safety guardrails that constrain developers and enterprises from fully utilising their capabilities.”
Most proprietary LLMs come with content or data protection guardrails, which could be more of a hindrance than a means of preventing misuse. For example, if company sales documentation is deleted or archived after a few years due to data protection, it is no longer accessible or useful to the LLM which needs that for subsequent training and fine-tuning. Policies aimed at preventing 'jailbreaking' of LLMs (deceiving the LLM into believing it is not bound by its content policy or use restrictions) can be so restrictive that they prevent legitimate and innovative uses of LLMs within the bounds of ethical and legal standards.
The ability of open-source LLMs to be customised by in-house development teams, the advantage of unnecessary guardrails, and growing community support, makes them a practical and appealing choice for businesses striving to stay competitive and innovative in the AI arena.
2. Rise of No-Code Custom LLMs in Business
In 2024, the rise of no-code and low-code platforms for customising LLMs is expected to significantly transform the business landscape.
A notable example is the Microsoft Azure AI Studio, which offers customisation and deployment options for LLMs through low-code/no-code interfaces. This platform simplifies the complex process of fine-tuning and customising models, essentially providing the 'plumbing layer' for LLMs. Similarly, Microsoft Copilot Studio stands as another example, empowering users to tailor AI capabilities to their specific enterprise needs without requiring extensive coding skills.
This trend is indicative of a broader movement in the enterprise AI space. It's not just about Microsoft leading the way; I anticipate that other major players like Amazon and Google, as well as emerging startups, will introduce similar customised no-code LLM offerings. These platforms will democratise access to advanced AI capabilities, enabling businesses of all sizes to experiment with and deploy LLMs swiftly and efficiently. They automate intricate processes like fine-tuning, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), and other customisations, making LLMs more accessible and adaptable to diverse business scenarios.
With these tools, companies can leverage the power of LLMs for various applications, from enhancing customer interactions to streamlining operational processes, without the barrier of high technical expertise. This democratisation signifies a pivotal shift towards a more intuitive and user-centric approach to AI in the business world, where the focus is on harnessing AI's potential in a way that aligns with specific business goals and strategies.
3. Multimodal Video Capabilities and Workflow Automation
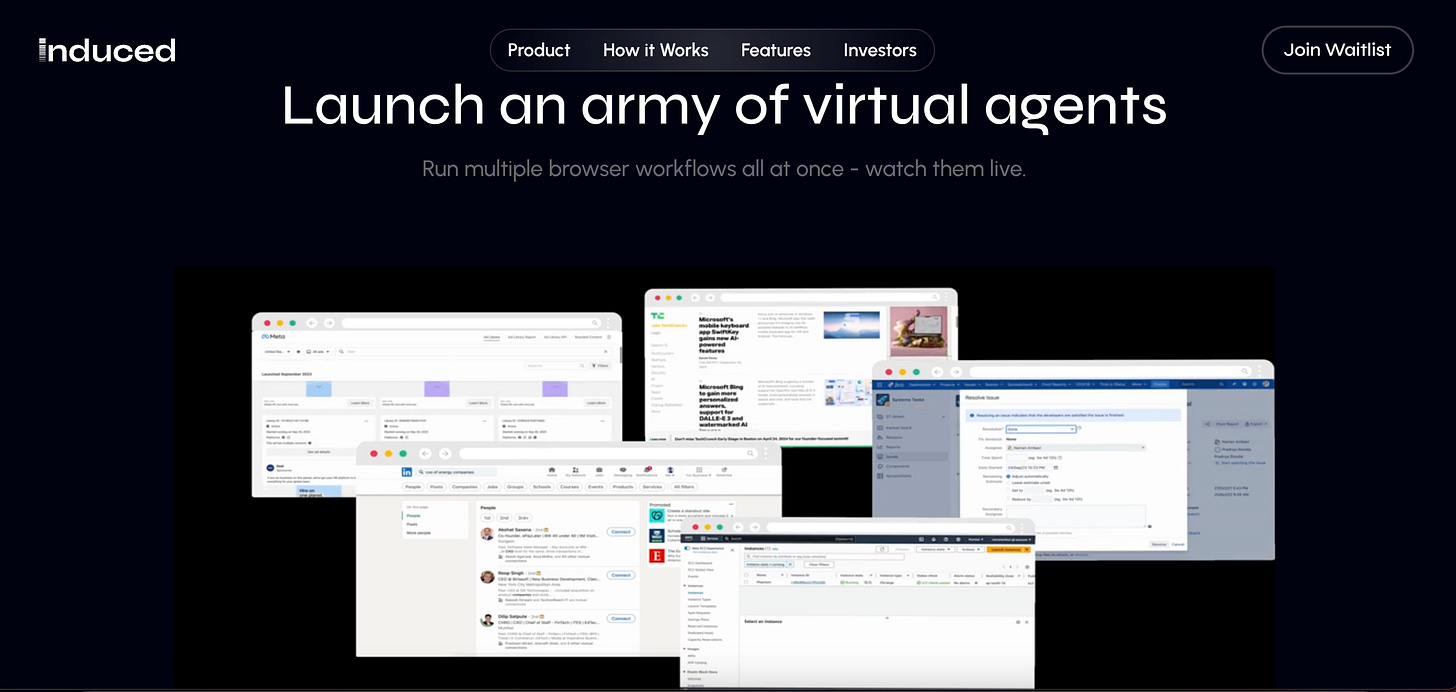
In 2024, I see the adoption of multimodal video capabilities in AI reaching new heights, revolutionising enterprise workflow automation. The integration of video input with LLMs, such as those seen in GPT-4 Turbo Vision and Gemini Ultra, allows businesses to analyse and utilise video data in real-time. For instance, GPT-4 Turbo Vision breaks down videos into frames for processing, and while Gemini Ultra’s multimodal video capabilities were faked in a video, it was an illustrative depiction of the possibilities of interacting with Gemini, based on real multimodal prompts and outputs from testing . Additionally, startups like Induced AI are harnessing video screen grabs of web-based workflows to drive automation.
The potential applications for multimodal LLM video capabilities are vast. They will transform computer vision video tasks in areas like robotics, healthcare, warehouse automation, autonomous driving amongst others. Perhaps the most significant impact will be in how enterprises utilise workflow and training videos. By feeding these videos into LLMs, businesses could significantly enhance their understanding and efficiency of internal processes, paving the way for full automation or optimised workflows, training and employee onboarding material.
4. The Shifting Landscape of RPA Industry
In 2024, the landscape of the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) industry is poised for a significant shift. Traditional RPA and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) systems, while efficient for structured and rule-based tasks, are increasingly limited by their inability to handle unstructured data and adapt to dynamic, changing environments. This is where advancements in LLMs and multimodal AI are starting to make a profound impact.
One such company that provides a glimpse of things to come in the RPA space is Sam Altman backed, Induced AI. Induced AI is integrating RPA and LLMs to create advanced automation tools. These tools can handle complex tasks and process various forms of data. Key capabilities include an AI-driven browser-based workflow automation tool that can interact with websites without an API, and the use of natural language descriptions to define tasks for RPA bots. Their tool uses browser instances to read on-screen content and control the browser in a manner similar to a human. This allows the browser instances to interact with websites even if they don’t have an API, thereby expanding the range of tasks that can be automated. This is a departure from traditional RPA solutions that rely on a lot of manual work to create rules.
LLMs, with their advanced capabilities in understanding context, reasoning, and task execution, are well-suited to address the complexities of unstructured data. They are capable of interpreting and processing a wide range of data types, from text and images to videos, making them versatile tools for various business applications. This versatility enables LLMs to perform tasks that require a level of understanding and adaptability beyond the scope of traditional RPA tools.
As LLMs continue to evolve, their role in enterprise automation strategies is will become more prominent. They offer a level of flexibility and efficiency that could see them taking the lead over RPA in certain areas, especially those involving complex decision-making or data interpretation tasks.
“Enterprises will consider LLMs as a more comprehensive solution for automating a broad range of business processes, potentially leading to a re-evaluation of RPA’s role within enterprise automation.”
5. Significant Breakthrough in AI Reasoning and LLM Arms Race
2024 is likely to be marked by a significant breakthrough in AI reasoning, fuelling a competitive environment among LLM providers. AI Orchestrators, as previously discussed, are expected to evolve into more sophisticated decision-makers and problem-solvers. LLMs, particularly those utilising Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting techniques, have already shown remarkable reasoning skills in arithmetic and symbolic tasks. However, they still face challenges in areas like action plan generation and complex reasoning.
To address these limitations, new approaches are being explored. For example, integrating LLMs with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) could enhance their reasoning on graph data. Additionally, methods like Q*, speculated to be developed by OpenAI, combine Q-learning and A* search algorithms, potentially leading to LLMs that can fully resolve complex reasoning tasks. Such improvements are expected to elevate the capabilities of LLMs, encouraging enterprises to adopt these advanced tools for strategic benefits as these capabilities start to get exposed through both proprietary LLMs and open source models in 2024.
“We should see the launch of GPT-5 in late 2024, and its key enhancement will be related to Q* and advanced reasoning capabilities.”
6. Coding LLMs Will Begin To Impact Tech Hiring
In 2024, I expect coding LLMs like GitHub Copilot, Replit AI, and Cursor AI to significantly impact tech hiring. GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI Codex, excels in context-based code suggestions, while Replit AI provides code generation and project-based suggestions. Cursor AI, featuring a ChatGPT sidebar, aids in code writing and debugging.
Other notable models like StarCoder and Code Llama are changing the game. StarCoder, known for its wide-ranging dataset training, excels in programming benchmarks and input processing. Code Llama, Meta's creation, is versatile across multiple programming languages.
For software teams that rely on conventional coding expertise, the integration of LLMs necessitates a strategic shift. Software teams will need to prioritise hiring for skills that complement LLM capabilities, such as high-level system design, LLM output integration, and strategic problem-solving. The focus will increasingly be on hiring people that who can oversee and enhance the LLM code outputs, ensuring they align with client requirements and project goals. Additionally, software teams will have to adapt to more agile and efficient workflows enabled by LLMs, which could lead to a transformation in project management and delivery processes.
“As the reliance on LLMs for coding and software development grows, educational institutions and training programs will need to update their curricula to include more on LLM integration and system design, aligning with the evolving demands of the industry.“
This shift is expected to cultivate a tech workforce in 2024 that is not only more innovative and efficient but also strategically equipped to harness the full potential of AI in software development and data science.
7. Aspirational AI Gaining Ground
The year 2024 is likely to mark a turning point in the AI debate with a shift towards Aspirational AI. This approach moves beyond the traditional confines of AI safety and responsible AI, which have often been characterised by a cautious and risk-averse perspective. Aspirational AI, in contrast, focuses on maximising AI's potential for positive impacts while managing risks in a balanced and responsible manner.
Aspirational AI aligns with broader trends like techno-optimism and Effective Accelerationism (e/acc), which advocate for harnessing technology to transcend human limitations and drive transformative change. This forward-looking approach to AI is about maximising its potential for positive impacts, aligning with the practical needs of businesses and the pursuit of innovation.
“Aspirational AI encourages exploring AI's capabilities to drive growth and solve complex challenges, representing a dynamic and proactive approach to AI. It's a mindset that sees AI not just as a tool for mitigating risks but as a driver of transformative change, contributing positively to business outcomes and societal progress.“
This perspective is increasingly resonating with companies and startups, as evidenced by the growing investment in AI technologies to create new opportunities and innovate in product and service offerings.
Enterprises adopting Aspirational AI will likely focus on leveraging AI to create new opportunities, innovate in product and service offerings, and improve operational efficiencies. This mindset shift represents a more dynamic and proactive approach to AI, where the emphasis is on harnessing its potential to contribute positively to business outcomes and societal progress. As such, Aspirational AI is set to become a more attractive and practical choice for businesses eager to explore the full spectrum of AI's capabilities in 2024 and beyond.
Wildcard Predictions
Here are my wildcard predictions for 2024. As we get closer to AGI, expect the unexpected. In times where paradigms are shifting its useful to expand your horizons and think outside the box.
1. Emergence of Non-Transformer AGI Companies
In 2024, the pursuit of AGI will expand beyond traditional transformer models, exploring novel computational approaches. Among these, probabilistic programming and message-passing techniques, reminiscent of the human brain's neocortex, show promise for expanding existing AI models in AGI capabilities. Additionally, mixed architectures are gaining attention, combining various models like transformers with "mixture of expert" systems to create more effective AI solutions. There's also a resurgence of interest in rule-based approaches, known as 'GOFAI' (Good Old-Fashioned AI), which were predominant in AI research until around 2010.
These diverse methods offer potential pathways to achieving more advanced, versatile, and efficient forms of AGI, broadening the scope of artificial intelligence beyond current paradigms.
“In 2024, I expect to see one of the non-transformer AGI approaches to be open sourced, allowing for further innovation and acceleration towards AGI.”
2. Foundational Model Company Acquires AI Chipset Capabilities
In 2024, the AI industry will witness an acquisition of an AI chipset company by a foundational model company. This move will combine advanced AI algorithms with state-of-the-art AI hardware. The integration of these two technologies will enhance the power, speed, and energy efficiency of AI models.
In terms of who acquires who, this is up for speculation and I will not get into names, but if I were to bet, it would be one of the up and coming foundational model companies that is well-funded and resourced. And in terms of the acquisition, look out for one of the many AI chipset companies that have started to ship or are close to taping out into AI data centre’s.
As explained in a previous newsletter, current LLMs are primed for substantial expansion, potentially up to three orders of magnitude, setting the stage for the development of a colossal $100 billion AI model by 2030. NVIDIA remains a dominant force in the AI chipset market, continuously enhancing its technical prowess. However, the key to maximising cost-efficiency and performance lies in the synergy between software and customised AI hardware. Optimising software to work inline with tailored AI chipsets will provide a competitive edge in harnessing the full potential of these advanced models.
However, this market shift is not without its challenges. The merger will likely raise concerns about a potential monopoly, as the combined entity will control significant aspects of both AI software and hardware.
Google is already operating on this model with its TPU hardware and Gemini model. So, this is not a unique capability and therefore I don’t see why one of the foundational model companies won’t push for AI chipset capabilities. One can argue whether Google has taken full advantage of this capability, but it certainly has a upper hand compared to its AI competitors.
Apple also follows the vertically integrated ‘software-hardware’ model for its products, and 2024 is likely to see Apple enter the fray with its own foundational model capabilities optimised for Apple chipsets.
“The question is whether Apple will expand its chipset capabilities from AI inference to AI training and data centre chipsets, which would be a game changer on all levels as it establishes itself in the AI space. And this line of questioning is also why a foundational model company will think seriously about acquiring AI chip capabilities.”
3. Quantum LLMs Will Speed Run AGI
One area that is likely to speed run AGI is quantum computing. This convergence of quantum computing and AI, particularly in LLMs and AGI, is driven by several groundbreaking developments in the past year.
Firstly, Google's Sycamore project has made significant strides, achieving what is known as 'quantum supremacy.' This term refers to a quantum computer's ability to perform calculations that would take traditional supercomputers an impractically long time to solve. Additionally, IBM's recent announcement of a quantum chip exceeding a 1,000-qubit quantum system indicates that we're rapidly approaching more powerful and capable quantum machines. This increase in qubits, the quantum equivalent of classical computing bits, promises more robust and complex quantum systems. Advancements in quantum error correction, a critical factor in making quantum systems reliable and practical for real-world applications, are also gaining momentum. This progress is essential for overcoming barriers in quantum computing's practical use.
Meanwhile, specific quantum algorithms designed for machine learning tasks are emerging. These algorithms allow AI systems to process data in higher-dimensional spaces more effectively than classical algorithms, enhancing their problem-solving capabilities and computational efficiency.
The integration of quantum computing with LLMs could offer significant improvements in several areas. Firstly, quantum computing's speed could enhance the efficiency of training and data processing for LLMs, allowing quicker analysis of large datasets. This enhancement is crucial for handling the computational demands of training larger models. Another key area is optimisation during model training. Quantum computing's ability to navigate vast solution spaces could help find optimal solutions more effectively, potentially leading to more accurate and robust LLMs. Additionally, quantum computing's suitability for high-dimensional data processing could aid LLMs in managing complex language structures more effectively. Energy efficiency is another potential benefit. Quantum computers could theoretically perform certain computations with greater energy efficiency than classical computers, making the operation of large-scale LLMs more sustainable.
Experts in the field, like John Roese from Dell Technologies and researchers at Fujitsu, are predicting that 2024 will be a pivotal year in this quantum-AI convergence. Their forecasts are based on the rapid advancements in both fields and the growing integration of quantum principles in AI algorithms.
4. Google Will Fail To Live Up To Gemini Hype
In 2024, Google's latest AI foundational model, Gemini faces a critical juncture with potential ramifications extending to the highest levels of the company's management. The challenges surrounding Gemini are multifaceted, involving market impact, intense competition, and internal coordination issues.
Gemini Pro's delayed launch and uncertain monetisation strategy have already hindered its market impact. The issues around Google's monetisation of Gemini primarily stem from the lack of a clear strategy, particularly in relation to its core search-based ad model. Uncertainties exist about how Gemini will be integrated into Google's existing products and services, and how this might disrupt current revenue streams.
The AI community's anticipation for Gemini Ultra in 2024 further overshadows Gemini Pro's current offerings. Without a clear and effective monetisation model, Gemini struggles to justify its high development costs and compete effectively in the rapidly evolving AI market.
The AI landscape is fiercely competitive, with players like OpenAI continually pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities. Gemini, despite its advancements, finds itself in a tight race against models like GPT-4 and also open source AI companies like Mistral.
Internally, Google has faced criticism and skepticism regarding Gemini’s capabilities. Inconsistencies in demonstrations and premature appearances in product rollouts suggest possible internal coordination and communication gaps. These issues not only affect Gemini deployment but also raise questions about Google's overall strategy and effectiveness in managing its AI developments.
Given these challenges, I see a high likelihood of a major management shake-up within Google in 2024. This could involve significant changes in the leadership of Google's AI divisions, including even a possible split of Google DeepMind or some of the DeepMind founders and employees leaving. With the AGI race heating up, competitive dynamics are going to heat up, and as we have seen in the recent months, tensions within company boards and management can blow over. Google is already under pressure with Sergey Brin known to be actively contributing to Gemini code development. I bet that we will likely see the return of Sergey Brin and Larry Page back to the helm in 2024.
5. OpenAI will be fully acquired by Microsoft
The possibility of OpenAI being fully acquired by Microsoft is increasingly likely in 2024, driven by a confluence of strategic and practical considerations. Central to this development is Satya Nadella's interest, as evidenced by his previous acqui-hire offer during OpenAI's management upheavals. This proposal, although not materialised then, set a precedent for future negotiations.
Sam Altman's role as OpenAI's leader is crucial in this scenario. His decision-making and influence over the company's direction and employee sentiment are pivotal. If Altman supports the merger, it's probable that a significant portion of OpenAI's staff would align with his decision, despite some existing reservations within the company. However, the internal dynamics of OpenAI's board and the resolution of past issues remain key factors that could sway the decision-making process.
Practical challenges faced by OpenAI, particularly in scaling up operations to meet the soaring demand for products like ChatGPT, significantly impact this potential merger. The organisation has been confronting limitations in GPU resources and data centre capacities. These challenges are expected to intensify with the development and impending launch of GPT-5, which will demand even more substantial computational resources.
Microsoft, with its vast capital reserves, extensive data centre infrastructure, and potential to acquire AI chipset companies, emerges as a fitting solution to these challenges. A merger with Microsoft would provide OpenAI the necessary resources to scale up efficiently and sustain the development and deployment of advanced AI models. This integration could also streamline OpenAI's operations, enabling them to focus on innovation and model development while leveraging Microsoft's infrastructure and financial muscle.
In summary, the merger between OpenAI and Microsoft is not just a strategic alignment but a practical necessity for OpenAI to overcome its scaling challenges and continue its trajectory in AI innovation.
6. Trump Victory Will Dial Back AI Regulations in the US
The potential re-election of Donald Trump in 2024 is expected to bring about a considerable shift in the regulatory landscape for AI in the United States. Trump, known for his pro-innovation and "America First" policies, will likely adopt a more laissez-faire approach towards AI, particularly in the realm of AGI and foundational models.
The Trump administration's stance is anticipated to contrast starkly with the more regulated approaches seen in Europe and under the Biden administration. By dialling back on AI regulations, the administration would enable a freer environment for AI innovation, focusing on maintaining America's competitive edge in technology. This approach argues against over-regulation, suggesting that such constraints can stifle innovation and hinder America's position in the global AI race.
One of the critical areas where this shift could be most evident is in the development and deployment of AGI systems. Trump's potential policy changes could result in looser controls over these technologies, allowing for more rapid advancement and application. This move could be seen as a boon for innovation in AI, particularly for Silicon Valley companies that are at the forefront of AGI research and development. This policy shift will likely encourage tech communities that are focused on techno-optimism and e/acc.
Additionally, Trump's approach to AI regulation is likely to diverge from Europe's stance on AI safety. While Europe has been proactive in implementing strict AI regulations to address ethical concerns and safety, the Trump administration may view such measures as unnecessary constraints that hamper the United States' ability to innovate and lead in the AI sector.
This is also in line with a shift in overall attitudes within the enterprise landscape of Aspirational AI, as discussed earlier, which promotes forward-looking innovation in AI, removing unnecessary shackles around ill-defined Responsible and Ethical AI policies.
In summary, Trump's re-election could mark a significant shift towards a more deregulated AI industry in the U.S., prioritising innovation and technological leadership. While this approach might raise concerns over AI safety and ethics, it could also spur rapid advancements and maintain the U.S.'s competitive edge in the global AI landscape.
I Value Your Perspectives!
Curious about your take on the wildcards and anticipated trends we've discussed. Agree, disagree, or have a different angle? Your viewpoints matter, and I'm eager to hear them in the comments below.
If you're finding these insights valuable, I'd appreciate if you could share them with your circles, both professional and personal. Your referrals are instrumental in growing our community and ensuring we stay at the forefront of GenAI and LLM developments.
Eagerly awaiting your thoughts and continued support!